
Embedded Insurance Gains Ground as a Key Growth Driver
Embedded insurance is reshaping the insurance industry, bringing coverage to consumers through everyday transactions and bridging the protection gap. With innovations in auto and mobility sectors, this approach aims to reach underserved customers, offering tailored solutions seamlessly integrated into purchases.
November 7, 2024
Auto
Insurance Industry
Risk Management
Technology

St. Petersburg Reduced Insurance Coverage for Tropicana Field Months Before Major Hurricane Damage
Ahead of the 2024 hurricane season, St. Petersburg reduced Tropicana Field’s wind and flood coverage from $100 million to $25 million, exposing the city to significant risk. After Hurricane Milton destroyed the stadium’s roof, officials now face uncertainties about potential coverage shortfalls.
November 5, 2024
Insurance Industry
Litigation
Property
Risk Management
Florida
NFIP Introduces Monthly Payment Option for Flood Insurance Policies
The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) will allow policyholders to pay flood insurance premiums monthly starting December 31, aiming to ease financial pressure on households and broaden access to flood coverage.
November 5, 2024
Insurance Industry
Legislation & Regulation
Property
Risk Management

Spain Sets $11.5 Billion Fund for Flood Relief Amid $20 Billion Loan Exposure
Following devastating floods in Valencia, Spain has announced an initial $11.5 billion aid package for affected communities, covering direct aid, credit guarantees, and municipal rebuilding. Officials anticipate further relief measures as cleanup continues.
November 5, 2024
Catastrophe
Insurance Industry
Legislation & Regulation
Property
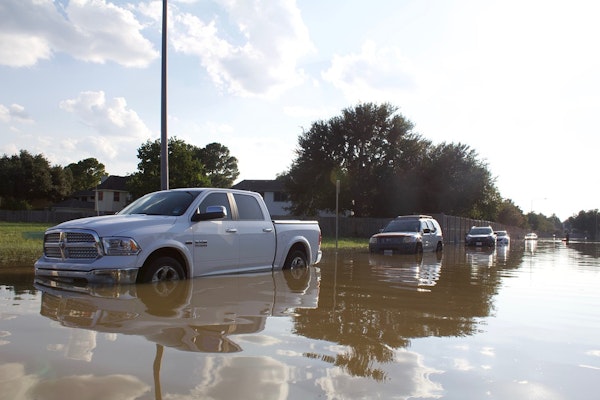

2024 Hurricanes Leave Nearly 350,000 Cars Flood-Damaged, CARFAX Warns
In 2024, hurricanes have left an estimated 347,000 vehicles with flood damage across the U.S., CARFAX reports. Experts caution that many may be resold, potentially concealing dangerous and costly water damage.
November 5, 2024
Auto
Catastrophe
Fraud
Risk Management
Florida

California’s Firefighting Crisis Highlights Need for Industry Support
California faces a severe shortage of wildfire firefighters, as low pay, mental strain, and challenging conditions drive workers away. Could the insurance industry help ease the burden on those protecting at-risk properties?
November 5, 2024
Catastrophe
Insurance Industry
Legislation & Regulation
Risk Management
California

Insurance Industry’s AI Progress: How Insurers Measure Up and What’s Next
While insurance ranks high in AI innovation, new research reveals the industry’s untapped potential to maximize AI-driven revenue and operational efficiency. With improvements in core functions like claims and underwriting, insurers are well-positioned yet still falling short in areas that could elevate them as AI leaders.
November 5, 2024
Insurance Industry
Technology
Underwriting

Insurers Navigate Risks and Opportunities in 2024 Global Report
The 2024 Global Insurance Report explores key shifts in the insurance sector, including market volatility, regulatory risks, low-carbon investments, and expanding private market exposure across various regions.
November 5, 2024
Life & Health
Property
Risk Management
Technology

Innovative AI Solution Takes Aim at Gun Violence Prevention
ZeroEyes, a tech company backed by The Institutes’ Predict & Prevent podcast, has developed AI-powered gun detection technology that combines human verification to curb gun violence. Through partnerships with schools and businesses, this system aims to protect communities, delivering alerts and minimizing bias by focusing solely on weapon detection.
November 5, 2024
Education & Training
Insurance Industry
Liability
Risk Management
Technology

Hailstorms Drive Record Insurance Losses as Experts Push for Better Detection and Prediction
Severe hailstorms in the U.S. have led to record insurance losses, with hail damage growing due to rising urbanization, climate change, and frequent severe convective storms. Enhanced monitoring projects promise insights to mitigate future risks.
November 5, 2024
Catastrophe
Insurance Industry
Risk Management
Technology
Colorado
Texas

Supreme Court Rejects Emergency Challenge to EPA Greenhouse Gas Standards for Power Plants
The U.S. Supreme Court recently declined to stay the EPA’s greenhouse gas emissions standards for coal-fired power plants, requiring plants expected to operate beyond 2039 to meet emission targets by 2032 or close by 2039. Legal challenges continue in lower courts.
November 5, 2024
Legislation & Regulation
Litigation
Risk Management

How Attorney Ads May Drive Up Auto Insurance Rates, Per New Survey
A recent IRC survey reveals that attorney advertising may be influencing auto insurance costs, as 60% of respondents link it to higher claims and 52% believe it raises insurance premiums.
October 30, 2024
Auto
Insurance Industry
Legislation & Regulation
Litigation
Florida
Georgia
Louisiana

Parametric Reputation Risk Insurance Expands to Cover "Metaphorical" Catastrophes
The 4-M parametric model, widely used for natural disaster insurance, is now being adapted to cover reputation risks, allowing businesses to mitigate financial impacts from reputational crises as effectively as from physical catastrophes.
October 30, 2024
Insurance Industry
Liability
Risk Management
Technology
Colorado

Embedded Insurance: The Key to Seamless Coverage for On-Demand Drivers
The on-demand economy is booming, yet drivers still face challenges accessing tailored auto insurance. Embedded insurance offers a seamless solution, streamlining coverage for the modern gig workforce.
October 30, 2024
Auto
Insurance Industry
Risk Management
Technology

Adapting to Virtual Construction Litigation: New Challenges and Prospects
The shift to virtual proceedings has reshaped construction litigation, offering cost savings and accessibility but also posing new challenges in case management, claims processing, and professional interactions.
October 30, 2024
Litigation
Technology





